дЄїи¶БзФ®жЭ•иЃ∞ељХеѓєжѓФзЫЃеЙНжµБи°МзЪДеПѓиІЖеМЦз±їеЇУжЄ≤жЯУ`еЕ≥з≥їеЫЊ`жЧґзЪДдЉШзЉЇзВєпЉМеМЕжЛђ D3пЉМEChartsпЉМG6з≠ЙгАВ
D3пЉИsvgпЉЙ
-------
жЦЗж°£пЉЪ[d3js.org/](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fd3js.org%2F "https://d3js.org/")
дЉШзВєпЉЪ
* еПѓеЃЪеИґз®ЛеЇ¶йЂШ
* svg еЬ®жХ∞жНЃйЗПе∞ПжЧґеЖЕе≠ШеН†зФ®жѓФ canvas дљО
зЉЇзВєпЉЪ
* svg еЬ®жХ∞жНЃйЗПе§ІжЧґжЄ≤жЯУдЉЪеН°й°њ
* йЬАи¶БиЗ™еЈ±еБЪжАІиГљдЉШеМЦ
EChartsпЉИcanvas/svgпЉЙ
-------------------
жЦЗж°£пЉЪ[echarts.apache.org/handbook/zhвА¶](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fecharts.apache.org%2Fhandbook%2Fzh%2Fget-started%2F "https://echarts.apache.org/handbook/zh/get-started/")
дЉШзВєпЉЪ
* еПѓдї•ж†єжНЃжХ∞жНЃйЗПиЗ™дЄїйАЙжЛ© canvas жИЦ svg жЄ≤жЯУ
* еѓєе§ІжХ∞жНЃжЄ≤жЯУжЬЙдЉШеМЦ
* жФѓжМБ webGLпЉИзЙєеИЂпЉЙ
зЉЇзВєпЉЪ
* еП™иГљзїШеИґеЇУйҐДиЃЊзЪДеЫЊи°®з±їеЮЛ
G6пЉИcanvasпЉЙ
----------
жЦЗж°£пЉЪ[antv-g6.gitee.io/zh/docs/manвА¶](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fantv-g6.gitee.io%2Fzh%2Fdocs%2Fmanual%2Fgetting-started%2F "https://antv-g6.gitee.io/zh/docs/manual/getting-started/")
дЉШзВєпЉЪ
* еЖЕзљЃ 9 зІНдЄАиИђеЫЊзЪДеЄГе±АеТМ 4 зІНж†СеЫЊзЪДеЄГе±АзЃЧж≥Х
* еѓєе§ІжХ∞жНЃжЄ≤жЯУжЬЙдЉШеМЦ
зЉЇзВєпЉЪ
* жЧ†йҐДиЃЊеی嚥
### еЄГе±АзЃЧж≥Х
[@antv/layout](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2Fantvis%2Flayout "https://github.com/antvis/layout")
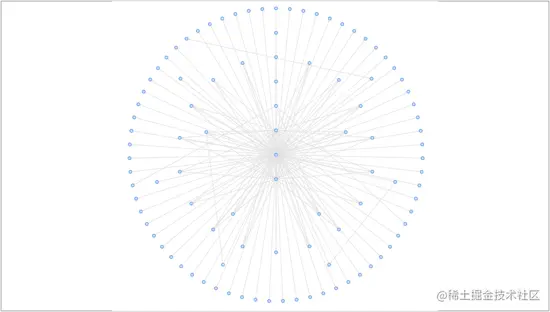
йЪПжЬЇпЉЪRandom еЄГе±АжШѓ G6 дЄ≠зЪДйїШиЃ§еЄГе±АжЦєж≥ХгАВељУеЃЮдЊЛеМЦеЫЊжЧґж≤°жЬЙжМЗеЃЪеЄГе±АжЦєж≥ХпЉМдЄФжХ∞жНЃдЄ≠дєЯдЄНе≠ШеЬ®дљНзљЃдњ°жБѓжЧґпЉМG6 е∞ЖиЗ™еК®дљњзФ® Random еЄГе±АгАВ
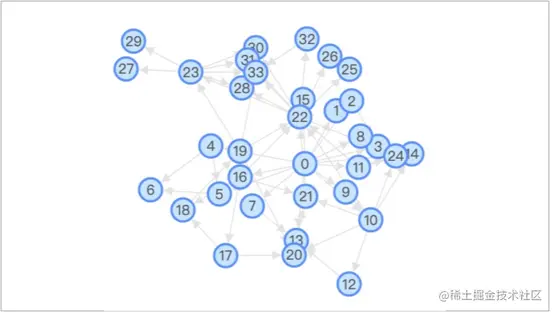
GForceпЉЪGForce еЃЮзО∞дЇЖзїПеЕЄзЪДеКЫеѓЉеРСзЃЧж≥ХпЉМG6 4.0 жФѓжМБгАВиГље§ЯжЫіеК†иЗ™зФ±еЬ∞жФѓжМБиЃЊзљЃиКВзВєиі®йЗПгАБзЊ§зїДдЄ≠ењГеКЫз≠ЙгАВжЫійЗНи¶БзЪДжШѓпЉМеЃГжФѓжМБ GPU еєґи°МиЃ°зЃЧгАВ
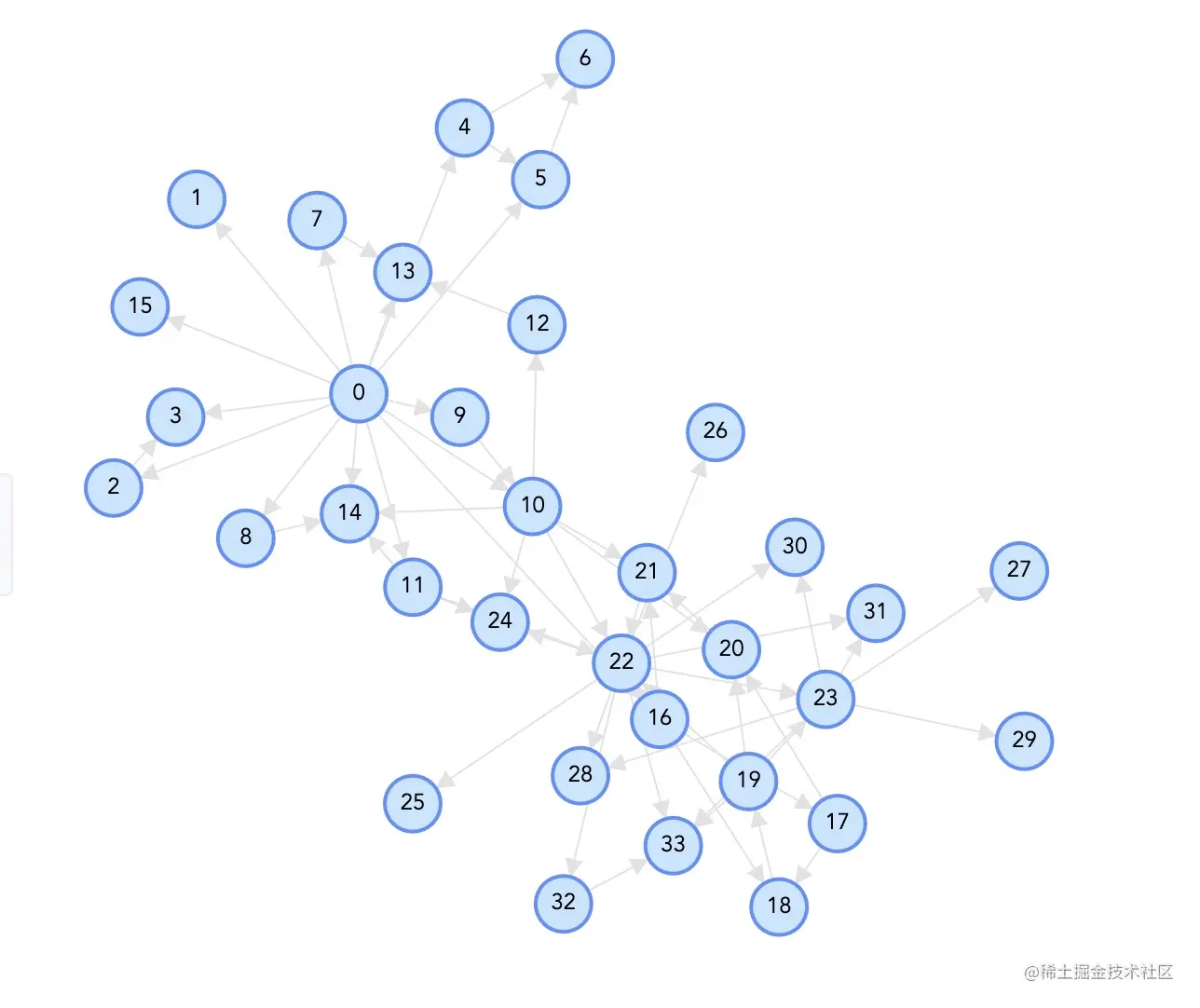
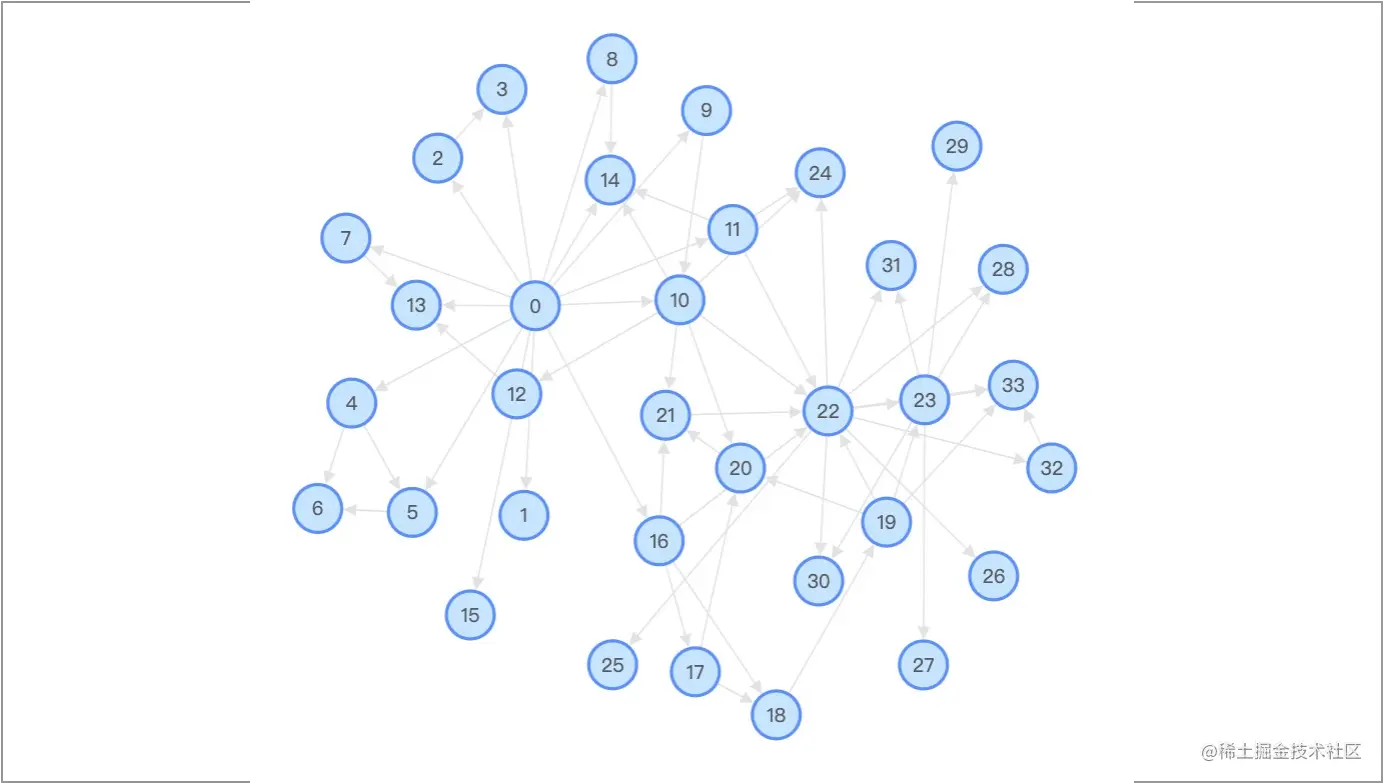
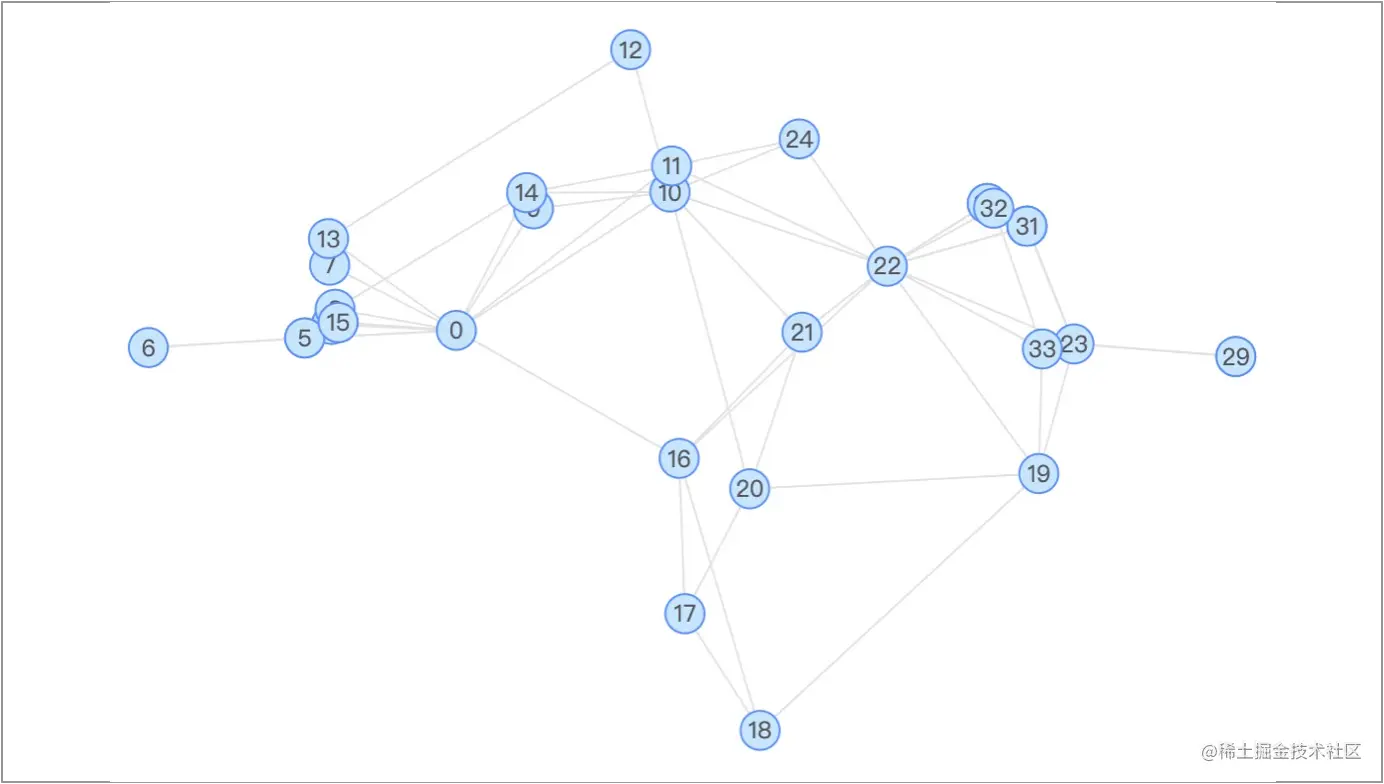
Force еКЫеѓЉеРСпЉЪForce еЄГе±АзїПеЕЄзЪДеКЫеѓЉеРСеЄГе±АжЦєж≥ХпЉМдЄО d3 зЪДеКЫеѓЉеРСеЄГе±АжЦєж≥ХзЫЄеѓєеЇФгАВеЕґе±ЮжАІдєЯдЄО d3.js зЪДеКЫеѓЉеЄГе±АеПВжХ∞зЫЄеѓєеЇФгАВ
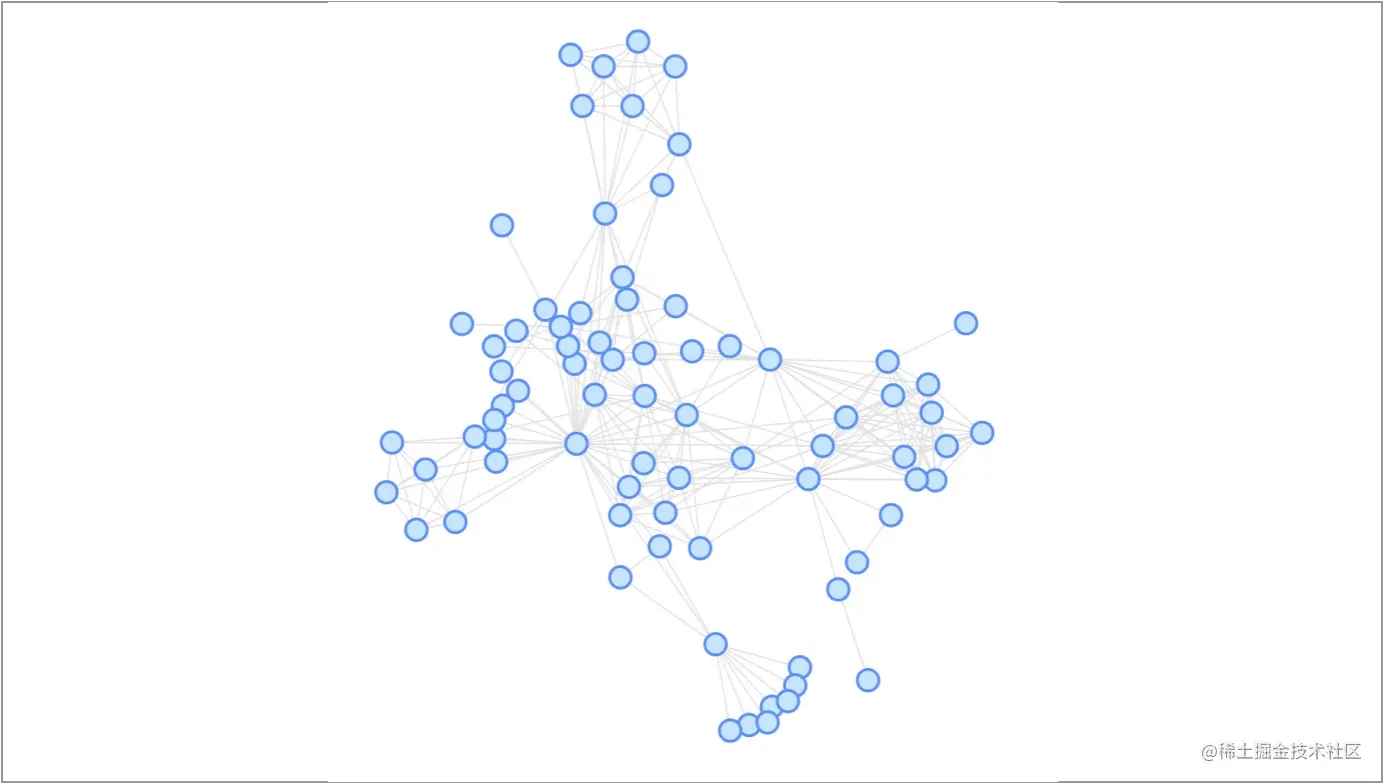
Force Atlas 2пЉЪForce Atlas 2 жШѓдЄАзІНеКЫеѓЉеРСеЄГе±АзЪДеПШ嚥пЉМжѓФ force жФґжХЫеЬ∞жЫіе•љпЉМжЫізіІеЗСгАВ
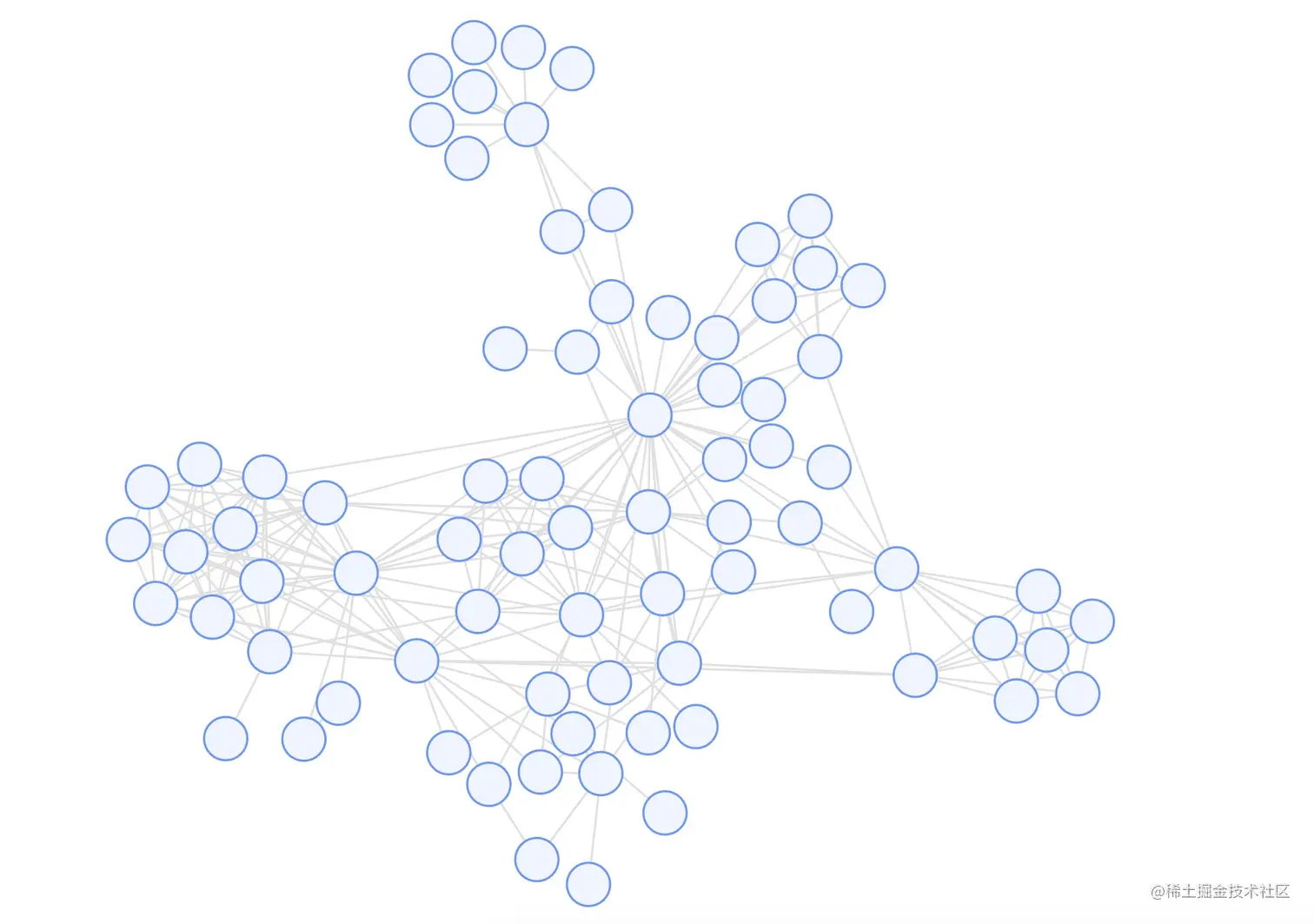
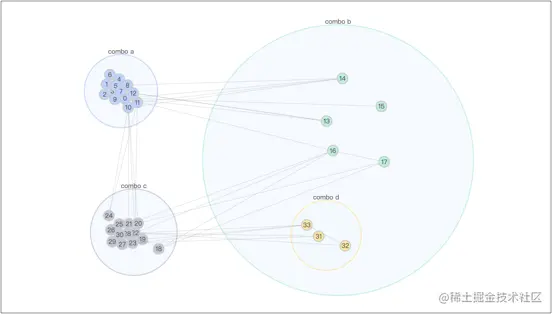
Combo еКЫеѓЉеРС ComboForceпЉЪComboForce жШѓеЯЇдЇОеКЫеѓЉеРСзЪДдЄУзФ®дЇОеЄ¶жЬЙ combo зЪДеЫЊзЪДеЄГе±АзЃЧж≥ХгАВйАЪињЗиЗ™з†ФжФєйА†зїПеЕЄеКЫеѓЉеРСзЃЧж≥ХпЉМе∞Жж†єжНЃиКВзВєзЪД combo дњ°жБѓпЉМжЦљеК†дЄНеРМзЪДеКЫдї•иЊЊеИ∞еРМ combo иКВзВєе∞љеПѓиГљиБЪйЫЖпЉМдЄНеРМ combo дєЛйЧіе∞љеПѓиГљжЧ†йЗНеП†зЪДеЄГе±АгАВ
FruchtermanпЉЪFruchterman еЄГе±АжШѓдЄАзІНеКЫеѓЉеЄГе±АгАВзЃЧж≥ХеОЯжЦЗпЉЪ [Graph Drawing by Force-directed Placement](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.mathe2.uni-bayreuth.de%2Faxel%2Fpapers%2Freingold%3Agraph_drawing_by_force_directed_placement.pdf "http://www.mathe2.uni-bayreuth.de/axel/papers/reingold:graph_drawing_by_force_directed_placement.pdf")
з΃嚥 CirculaпЉЪCircular еЄГе±Ае∞ЖжЙАжЬЙиКВзВєеЄГе±АеЬ®дЄАдЄ™еЬЖзОѓдЄКпЉМеПѓдї•йАЙжЛ©иКВзВєеЬ®еЬЖзОѓдЄКзЪДжОТеИЧй°ЇеЇПгАВеПѓдї•йАЪињЗеПВжХ∞зЪДйЕНзљЃжЙ©е±ХеЗЇзОѓзЪДеИЖзїДеЄГе±АгАБиЮЇжЧЛ嚥еЄГе±Аз≠ЙгАВеОЯжЦЗйУЊжО•пЉЪ [A framework and algorithms for circular drawings of graphs](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%2Fscience%2Farticle%2Fpii%2FS1570866705000031 "https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1570866705000031")гАВ

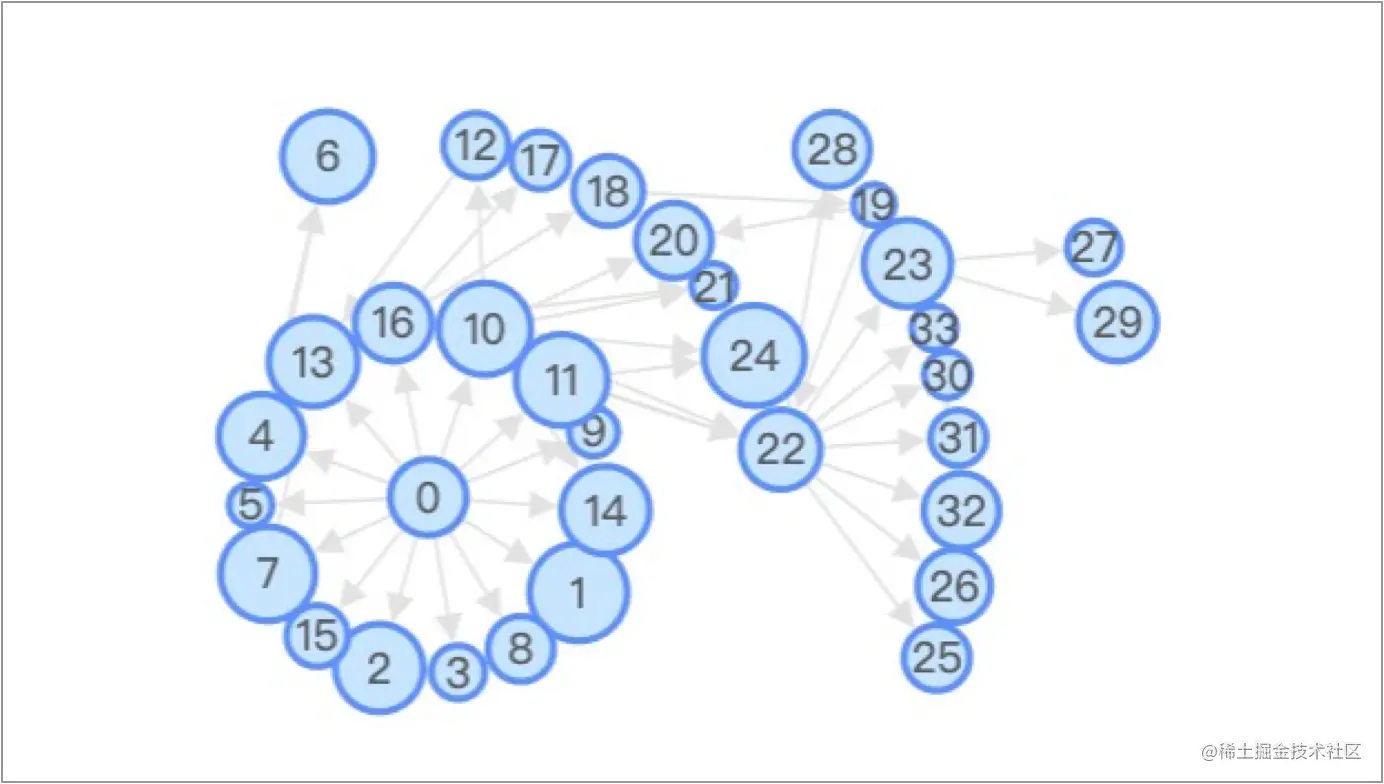
иЊРе∞Д嚥 RadialпЉЪRadial еЄГе±АжШѓе∞ЖеЫЊеЄГе±АжИРиЊРе∞ДзКґзЪДеЄГе±АжЦєж≥ХгАВдї•дЄАдЄ™ focusNode дЄЇдЄ≠ењГпЉМеЕґдљЩиКВзВєжМЙзЕІдЄО focusNode зЪДеЇ¶жХ∞еЕ≥з≥їжОТеИЧеЬ®дЄНеРМиЈЭз¶їзЪДзОѓдЄКгАВиЈЭз¶ї focusNode дЄАеЇ¶зЪДиКВзВєеЄГе±АеЬ®дЄОеЕґжЬАињСзЪДзђђдЄАдЄ™зОѓдЄКпЉМиЈЭз¶ї focusNode дЇМеЇ¶зЪДиКВзВєеЄГе±АеЬ®зђђдЇМдЄ™зОѓдЄКпЉМдї•ж≠§з±їжО®гАВзЃЧж≥ХеОЯжЦЗйУЊжО•пЉЪ [More Flexible Radial Layout](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=http%3A%2F%2Femis.ams.org%2Fjournals%2FJGAA%2Faccepted%2F2011%2FBrandesPich2011.15.1.pdf "http://emis.ams.org/journals/JGAA/accepted/2011/BrandesPich2011.15.1.pdf")гАВ
еРМењГеЬЖ ConcentricпЉЪConcentric еЄГе±АдЄЇеРМењГеЬЖеЄГе±АпЉМзФ®жИЈеПѓдї•жМЗеЃЪиКВзВєжЯРдЄ™е±ЮжАІдЄЇжОТеЇПдЊЭжНЃпЉИйїШиЃ§дЄЇиКВзВєеЇ¶жХ∞ degreeпЉЙпЉМиѓ•е±ЮжАІеАЉиґКйЂШпЉМеИЩиѓ•иКВзВєеЄГе±АеРОзЪДдљНзљЃдЄ≠ењГгАВ
йЂШзїіжХ∞жНЃйЩНзїі MDSпЉЪMDS еЄГе±АжШѓйЂШзїіжХ∞жНЃйЩНзїізЃЧж≥ХеЄГе±АпЉМиѓ•зЃЧж≥ХеЕ®зІ∞ Multidimensional Scaling гАВ
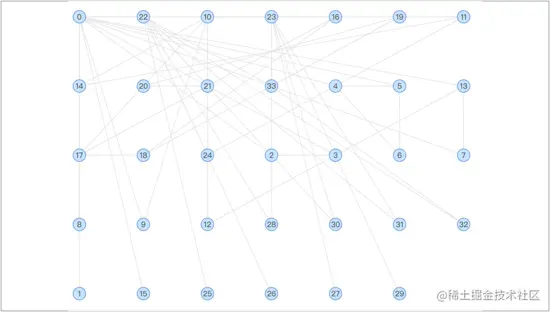
ж†Ље≠Р GridпЉЪGrid еЄГе±АжШѓе∞ЖжЙАжЬЙиКВзВєйАЪињЗжЯРзІНжМЗеЃЪе±ЮжАІжОТеЇПеРОпЉМжХійљРеЬ∞жФЊзљЃеЬ®зљСж†ЉдЄКгАВ
| - | D3 | ECharts | G6 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| жЄ≤жЯУжЦєеЉП | svg | svgгАБcanvas | canvas |
| еПѓеЃЪеИґз®ЛеЇ¶ | йЂШ | иЊГйЂШ | иЊГйЂШ |
| еЄГе±АзЃЧж≥Х | жЧ† | жЧ† | жЬЙ |
| е§ІжХ∞жНЃжЄ≤жЯУдЉШеМЦ | жЧ† | жЬЙ | жЬЙ |
* [antv.vision/zh](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fantv.vision%2Fzh "https://antv.vision/zh")
* [observablehq.com/@d3/gallery](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fobservablehq.com%2F%40d3%2Fgallery "https://observablehq.com/@d3/gallery")
* [echarts.apache.org/handbook/zhвА¶](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fecharts.apache.org%2Fhandbook%2Fzh%2Fbasics%2Frelease-note%2Fv5-feature%2F "https://echarts.apache.org/handbook/zh/basics/release-note/v5-feature/")
* [graphin.antv.vision/graphin/layвА¶](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fgraphin.antv.vision%2Fgraphin%2Flayout%2Fnetwork "https://graphin.antv.vision/graphin/layout/network")
* [vleedesigntheory.github.io/tech/front/вА¶](https://link.juejin.cn/?target=https%3A%2F%2Fvleedesigntheory.github.io%2Ftech%2Ffront%2Fgraph20210419.html%23%25E5%25B8%25B8%25E8%25A7%2581%25E7%25AE%2597%25E6%25B3%2595 "https://vleedesigntheory.github.io/tech/front/graph20210419.html#%E5%B8%B8%E8%A7%81%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95")
